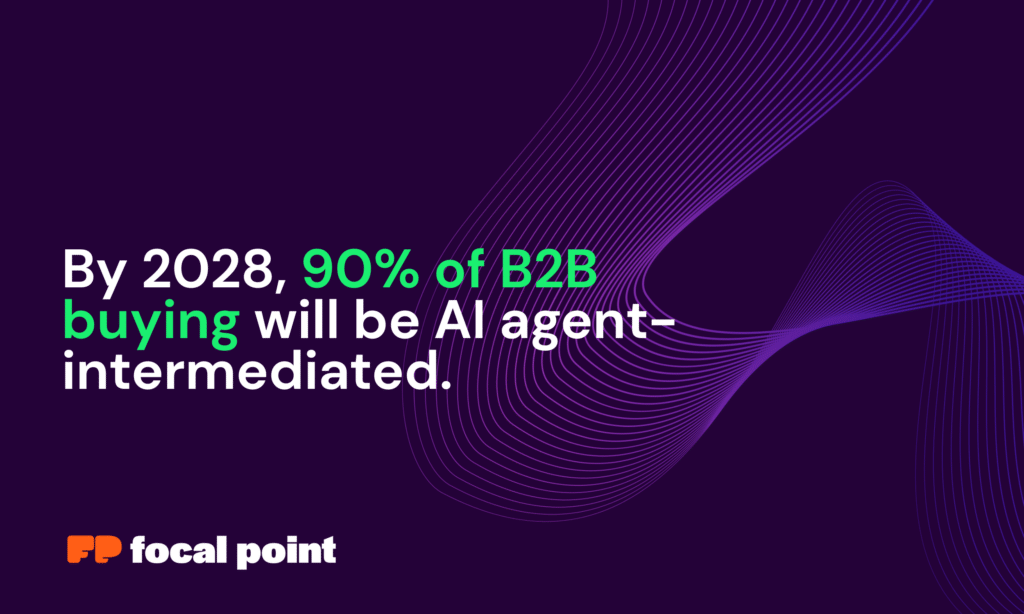
Did you know that Gartner predicts by 2028, 90% of B2B buying will be AI agent-intermediated, pushing over $15 trillion in B2B spend through AI agent exchanges? This ambitious prediction highlights the transformative shifts reshaping the procurement landscape predicted for 2026.
We’re witnessing a pivotal moment in procurement history: as we look ahead through 2026 and beyond, the industry is experiencing an unprecedented acceleration driven by agentic AI, autonomous digital workers, and intelligent orchestration. Procurement’s traditional role as a cost-cutting function has fully evolved into a strategic powerhouse, helping organizations balance profitability with sustainability goals while navigating increasing global complexity.
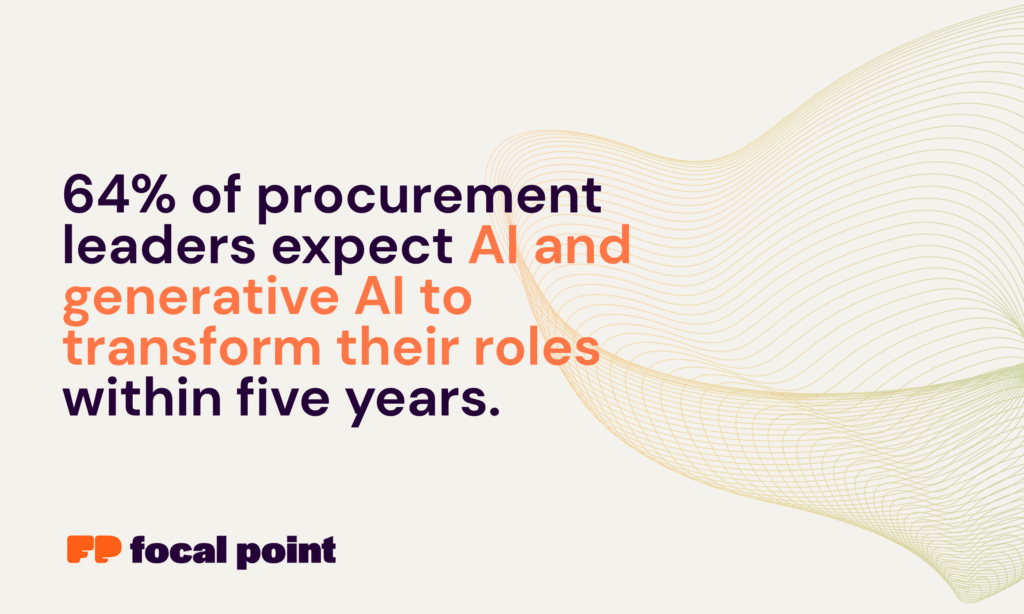
Recent research cited by AI at Wharton indicates that 94% of procurement teams and decision makers already use generative AI tools at least once a week. Meanwhile, The Hackett Group’s 2025 Key Issues Study shows that 64% of procurement leaders expect AI and generative AI to transform their roles within five years, and 89% of executives are advancing GenAI initiatives across the enterprise, up from just 16% the prior year. This isn’t experimentation anymore, it’s operationalization at scale.
The question has shifted from “Should we use AI?” to “Which processes are AI-first by design?”
In this article, we’ll dive into the key procurement trends shaping the industry’s future in 2026. We’ll examine the rise of agentic AI, the growing importance of orchestration layers, and how sustainability is moving from measurement to scalable action. These changes will redefine procurement’s role in driving business success.
- AI and The Digital Transformation Revolution Enters the Agentic Era
- From AI Tools to AI Agents: The Operationalization Imperative in 2026
- The Composable Tech Stack: Orchestration > Monoliths
- The New Procurement Skillset: AI Fluency + Strategic Judgment = Success
- The Strategic Imperative: CPOs as Enterprise Value Architects
- Category Management Reimagined: From Static Strategies to Dynamic Execution
- Risk Management and Resilience: From Periodic Assessment to Continuous Vigilance
- ESG in Procurement: From Disclosure to Commercial Accountability
- Supplier Collaboration and Sustainability: The Engine of Sustainable Transformation
- The Procurement Workforce: Building Teams for the Agentic Era
- Operational Excellence: The Orchestration Advantage
- Data-Driven Decision Making: The Foundation of Intelligent Procurement
- Summary: Procurement's Defining Year
- FAQ
AI and The Digital Transformation Revolution Enters the Agentic Era
The procurement landscape has radically shifted as AI in procurement moves beyond experimentation into full-scale operationalization. We’re no longer talking about AI-powered features bolted onto existing tools, we’re witnessing the emergence of agentic AI: autonomous digital workers capable of understanding context, making decisions, taking actions across systems, and keeping work moving without waiting on a human to push a button.
Digital transformation is no longer a buzzword; it’s the operational reality. Gartner predicts that by 2028, approximately one-third of enterprise applications will include agentic AI features, which could allow around 15% of daily work decisions to happen automatically. For procurement, this means digital operating models are moving faster than ever, and teams that delay adoption risk falling behind competitors who use intelligent systems to speed up cycle times, gain better insights, and strengthen supplier relationships.
McKinsey highlights that organizations deploying AI-driven analytics in procurement can unlock around 20% savings potential and significantly accelerate processes such as supplier selection, in some cases by roughly 30%.
Analysts forecast rapid uptake of AI-driven analytics in procurement over the next few years, with functions that invest early seeing noticeably higher cost savings and efficiency gains.
The impact of agentic AI extends throughout the procurement process:
- Intelligent intake and triage: Auto-classification of requests, validation of mandatory fields, and prioritization based on SLAs and business rules
- Automated supplier research: Pulling risk data, summarizing supplier profiles, and identifying alternatives in minutes rather than weeks
- Document generation: Drafting RFP packages, creating scoring rubrics, and generating negotiation prep materials
- Project coordination: Updating status from email and Slack, triggering next-step tasks, and monitoring timelines for risks
- Continuous compliance monitoring: Real-time validation against company policies and regulatory requirements
As we move through 2026, the focus is shifting from siloed AI tools to end-to-end orchestration. This transition is creating new efficiencies and insights, transforming procurement from a cost center to a strategic value creator.
While the benefits are clear, concerns about data security, governance, and responsible AI use continue to rise. A 2025 EY survey found that nearly all large companies deploying AI reported some risk-related financial loss, from compliance failures to flawed outputs. Organizations with stronger “Responsible AI” frameworks performed better across cost savings and operational outcomes, underscoring that AI advancement works better and more responsible governance keeps pace.

From AI Tools to AI Agents: The Operationalization Imperative in 2026
AI integration in procurement processes has moved from pilot programs to production deployments. A Deloitte survey found that 92% of Chief Procurement Officers are planning and assessing generative AI capabilities, with 22% of CPOs planning to invest more than $1 million annually in GenAI by 2025. But the teams that will come out on top in 2026 are focused on operationalization.
Traditional AI tools (chatbots, copilots, and autocomplete features) still rely on human initiation and oversight for every action. True AI agents are autonomous digital workers that can receive a goal, reason with context, make decisions, perform actions across systems, and collaborate with humans or other agents. Each agent is designed to do one job exceptionally well.
What AI Agents Are:
- Autonomous systems capable of multi-step reasoning and execution
- Context-aware workers that understand procurement policies and business rules
- Cross-system operators that can act across ERPs, contract repositories, intake tools, and communication platforms
What AI Agents Are Not:
- Chatbots (conversation only, no true action)
- Copilots (helpful assistants but reliant on human initiation)
- RPA/Bots (rule-based automation with no reasoning)
- Autocomplete AI (simple responses without system integration)
AI-powered tools are making significant inroads across procurement workflows. Organizations report using AI for spend analysis to identify inefficiencies and reduce costs, forecasting and demand planning using historical data and market trends, risk management through continuous monitoring of supplier data, and compliance monitoring to adhere to procurement regulations.
Despite the varied benefits, data privacy and governance remain critical concerns. Research shows that over 25% of companies have restricted or banned certain generative AI tools due to privacy issues, while 63% limit the types of data employees can input into AI systems. As AI integration deepens, striking a balance between innovation and data protection will be critical for successful procurement automation.
The organizations seeing the greatest returns are those reimagining procurement around AI capabilities rather than simply automating existing processes. The greatest value comes from augmenting (not replacing) procurement professionals. By automating routine tasks and providing superior analytics, AI frees teams to focus on strategic activities where human judgment adds the most value.
The Composable Tech Stack: Orchestration > Monoliths
Cloud procurement systems, orchestration layers, and predictive analytics are leading procurement’s digital transformation in 2026. The era of “rip and replace” mega-suites is giving way to composable, API-first ecosystems that boost efficiency, transparency, and strategic decision-making.
The Rise of Orchestration Layers
The primary failure point for most AI initiatives is a lack of integration. Agents can only perform as well as the information and context they can access, and procurement data is notoriously scattered across ERPs, contract repositories, intake tools, spreadsheets, inboxes, and supplier systems. When underlying data is fragmented, even the most advanced AI produces inconsistent or limited value.
This is why orchestration layers have become critical infrastructure for 2026. An effective orchestration platform serves as the central coordination system that manages workflow dependencies, compliance requirements, SLA tracking, human approvals, audit trails, and global status visibility. It ensures AI agents operate safely, accurately, and in context, ultimately enabling true multi-agent collaboration.
Platforms like Focal Point provide enterprise-level orchestration capabilities from a single window, integrating with existing processes and offering one place to manage all procurement needs without disruption. Through no-code configurations, teams can customize workflows without technical expertise, making it possible to adapt and evolve processes as needs change.
Cloud-Based Procurement Systems
Cloud procurement solutions continue to offer scalability and real-time collaboration. They enable quick responses to market shifts and reduce infrastructure costs. In 2026, cloud-native systems are the norm, allowing teams to access data and tools anytime, anywhere while providing the foundation for AI agent deployment.
Predictive Analytics and Continuous Intelligence
Predictive analytics is transforming procurement strategies beyond periodic reporting to continuous intelligence. By analyzing historical data, market trends, and real-time signals, teams can forecast demand more accurately, anticipate supply disruptions, and optimize purchasing decisions. This leads to smarter sourcing, reduced costs, and better inventory management.
Unified Data Layer Benefits
A unified data layer offers complete visibility across operations. It merges data from various sources (ERP and P2P systems, best-of-breed point solutions, and third-party data providers) giving a comprehensive view of procurement activities. This unification enables better decision-making and represents a radical shift from the fragmented point-solution approach that held many teams back.
Integration Capabilities
System integration remains vital for a comprehensive procurement ecosystem. Seamless integration with ERP and CRM systems improves coordination and data flow. But in 2026, integration goes beyond connecting systems, it means providing AI agents with the context they need to make intelligent decisions. Without clean data and proper orchestration, AI and advanced analytics simply won’t deliver on their promise.
The New Procurement Skillset: AI Fluency + Strategic Judgment = Success
As the procurement landscape evolves, effective organizations demand a fresh set of skills for professionals in 2026. As agentic AI reshapes the industry, we’re witnessing a fundamental shift in what it means to be a procurement professional. Digital literacy and AI fluency have moved from “nice to have” capabilities to core job requirements.
Deloitte’s latest CPO survey highlights digital literacy and AI fluency as core skills for tomorrow’s teams, not fringe capabilities reserved for technical specialists. The baseline has risen: comfort with data, tools, and change is now part of the job description, not an optional extra.
AI Management and Data Interpretation
In 2026 and beyond, procurement professionals must master AI management and data interpretation. These skills are crucial for leveraging AI-driven insights and making informed decisions. But mastery doesn’t mean becoming a data scientist, it means understanding how to work effectively alongside AI agents, knowing when to trust automated recommendations, and recognizing when human judgment must override algorithmic outputs.
Strategic thinking becomes even more vital as teams navigate complex supplier relationships and market dynamics. The professionals who thrive will be those who can translate AI-generated insights into actionable business strategies.
Emerging Roles in Procurement
In 2026, expect to see new specialized roles emerging across procurement organizations:
- Procurement data translators who turn analytics into action and bridge the gap between technical outputs and business decisions
- Automation and AI product owners for source-to-pay workflows who manage agent deployment, monitor performance, and continuously optimize AI capabilities
- Supplier risk and ESG specialists embedded in category teams who combine technical compliance knowledge with strategic supplier relationship skills
- Orchestration architects who design and maintain the workflows, integrations, and governance frameworks that enable AI agents to operate effectively
Training and Adaptation Strategies
To prepare for this AI-driven future, organizations are implementing comprehensive training programs focused on safe AI experimentation and hands-on learning experiences. The most successful approaches recognize that transformation is about building confidence and changing mindsets.
Leading organizations are investing in workforce readiness, operating-model redesign, and cross-functional change management to ensure AI becomes embedded in everyday decision-making. As AI capabilities become more widely available, competitive advantage will hinge less on the tools themselves and more on how organizations adopt them.
Balancing Human Expertise with AI Capabilities
Successful human-AI collaboration in procurement requires a deliberate balance. Teams must align AI strategies with procurement goals while preserving human judgment for complex negotiations, relationship management, and ethical decision-making. This approach ensures that AI enhances rather than replaces human expertise, leading to more effective outcomes.
Agentic AI, when implemented correctly, amplifies human expertise by handling the executional and tactical load that slows teams down, freeing procurement professionals to focus on strategic work where their judgment adds the most value.
Soft Skills Remain Essential
While technical capabilities are increasingly important, soft skills (stakeholder management, storytelling, negotiation, and cross-functional collaboration) remain crucial. The difference in 2026 is that these skills must now be combined with digital fluency. The procurement professional who can negotiate a complex supplier agreement and understand how to leverage AI for contract analysis will outperform specialists in either domain alone.
Success Metrics and Benchmarks
To measure the impact of AI integration and skills development, procurement teams are developing new performance metrics. These include improved efficiency in procurement processes, cost savings through AI-driven insights, enhanced supplier relationship management, increased accuracy in demand forecasting, and time reallocation from tactical to strategic activities.
The teams that invest in developing this blended skillset, technical fluency combined with strategic judgment, will be positioned to lead procurement’s continued evolution.
The Strategic Imperative: CPOs as Enterprise Value Architects
Procurement professionals know that strategic procurement has evolved far beyond cost-cutting. As the function continues to evolve toward value creation throughout the supply chain, we’re seeing the CPO role transform into something that increasingly mirrors the leadership agenda of a CEO.
According to BCG’s Inverto 2026 procurement trends research, CPOs are rapidly becoming enterprise leaders, shaping resilience, AI adoption, and supplier ecosystems that drive organizational performance. The path between CPO and CEO has never been closer. Procurement now shapes decisions that influence margins, quality, risk exposure, and growth potential, responsibilities that extend well beyond traditional sourcing activities.
From Cost Center to Value Creator
The digital technologies reshaping procurement offer access to previously unavailable data and enable more sophisticated analysis. This data-driven approach is revolutionizing procurement strategy, enabling proactive decision-making and scenario prediction rather than reactive responses to market conditions.
With the rise of agentic AI and procurement automation, transactional activities are increasingly handled by intelligent systems, freeing teams to focus on deeper category insights, innovation partnerships, and strategic decision-making. The procurement function is no longer defined by administrative tasks but by the value it creates across the business.
Long-Term Value-Driven Relationships
Strategic procurement in 2026 emphasizes building long-term partnerships that go beyond price negotiations. These relationships prioritize innovation, reliability, risk mitigation, and shared sustainability goals. Supplier choice is no longer just about today’s performance, it shapes the future operating model and the organization’s ability to innovate at speed and scale.
Organizations are recognizing that their most strategic suppliers are partners in transformation, not just vendors to be managed. This shift requires procurement teams to develop new capabilities in supplier development, collaborative innovation, and relationship orchestration.
Metrics for Measuring Value Creation
To assess the impact of strategic procurement, organizations are adopting performance metrics that move beyond simple cost reduction:
- Cost savings and cost avoidance percentages
- Innovation contributions from supplier partnerships
- Sustainability and ESG improvements across the supply chain
- Supplier relationship health scores
- Risk mitigation and resilience indicators
- Speed-to-value on strategic initiatives
- Stakeholder satisfaction and cross-functional collaboration effectiveness
Strategic Decision-Making Frameworks
Procurement teams are using data-driven insights to inform strategic decisions through sophisticated frameworks. These encompass risk assessment models that factor in geopolitical, financial, and operational variables; total cost of ownership analyses that include sustainability impacts; long-term value considerations beyond immediate savings; and cross-functional collaboration metrics that measure procurement’s enterprise impact.
The most advanced organizations are embedding AI-driven insights into these frameworks, enabling real-time scenario planning and dynamic strategy adjustment as market conditions change.
Role of Procurement in Business Strategy
Procurement’s influence on enterprise strategy continues to expand. Chief Procurement Officers are now viewed as “chief value officers” who drive organizational success through multiple channels:
- Business partnering initiatives that align procurement activities with enterprise objectives
- Digital technology adoption that enables AI-driven efficiency and intelligence across operations
- Sustainability programs that deliver measurable ESG outcomes while supporting business goals
- Supply chain resilience that protects the organization from disruption while maintaining competitive flexibility
- Innovation enablement through strategic supplier partnerships and ecosystem development
The Orchestration Advantage
As AI’s role in procurement expands beyond individual use cases, what once existed as isolated tools is now forming connected value chains. These link demand insights, automated should-costing, AI-guided negotiations, specification optimization, and supplier collaboration into cohesive workflows.
Platforms like Focal Point enable this orchestration by providing enterprise-level capabilities from a single window, connecting people, processes, and data across the procurement ecosystem. This unified approach allows procurement teams to execute on strategic priorities rather than spending time navigating fragmented systems and manual handoffs.
Tomorrow’s AI strategy will be written not only in contracts but in how procurement enables people, processes, and partnerships to transform. The organizations that recognize procurement as a strategic function and invest accordingly will be positioned to outperform competitors who still view it as a transactional necessity.
Category Management Reimagined: From Static Strategies to Dynamic Execution
Category management is becoming increasingly critical to the strategic procurement conversation in 2026. With the right category strategies powered by intelligent technology, procurement teams are capable of generating significant strategic value. This is reshaping how organizations handle their spend categories, moving from annual planning cycles to continuous optimization.
Technology-Enabled Category Management
The integration of built-for-purpose tools is revolutionizing category management. Analytics and business intelligence platforms are now essential for visualizing spend data, tracking performance metrics, and identifying optimization opportunities in real time. These tools enable procurement teams to identify the crucial 20% of suppliers that typically account for 80% of total spend, allowing for more focused management strategies.
But in 2026, technology goes beyond analytics dashboards. Agentic AI is transforming how category strategies are developed and executed. AI can now analyze internal spend data alongside external market signals to help teams build and evolve category strategies dynamically. Whether focused on sourcing sustainably, consolidating suppliers, or driving innovation partnerships, AI helps procurement move from static slides to dynamic execution.
Platforms like Focal Point turn category strategy into action with AI that understands organizational goals. By connecting category plans to daily workflows, intake requests, and supplier data, teams can ensure every decision aligns with strategic priorities.
Cross-Functional Collaboration
Effective category management in 2026 requires increased collaboration across departments. Procurement teams are working closely with IT, finance, legal, sustainability, and business units to navigate complex operating environments and deliver enterprise-wide value. This cross-functional approach ensures that category strategies align with broader business goals and adapt to rapid market changes.
The most successful category managers are those who can facilitate collaboration across organizational boundaries, translating procurement insights into language that resonates with diverse stakeholders. AI-powered tools support this collaboration by providing shared visibility into category performance, supplier health, and market dynamics.
Data-Driven Category Strategies
Data-driven strategies are at the heart of modern category management. Procurement teams are using market intelligence metrics to understand spending patterns, track pricing trends, assess supplier risks, and identify consolidation opportunities. In categories with high spend variability, such as travel, fleet, marketing services, and IT, these insights are crucial for preventing fragmented spending and optimizing total cost of ownership.
In 2026, leading organizations are augmenting traditional category analysis with AI-driven capabilities:
- Automated market intelligence that continuously monitors pricing trends, supplier news, and competitive dynamics
- Predictive demand modeling that anticipates category needs based on historical patterns and business forecasts
- Scenario planning tools that model the impact of supplier changes, market disruptions, or strategic shifts
- Sustainability impact analysis that evaluates category decisions against ESG goals and carbon reduction targets
New Category Management KPIs
As we move into 2026, the focus is shifting from traditional hard savings to more nuanced procurement KPIs. These emphasize value creation, supplier innovation contributions, risk mitigation, and sustainability outcomes alongside cost performance. This evolution reflects a more sophisticated approach to category management—one that balances immediate financial returns with long-term strategic positioning.
Progressive organizations are measuring category success through metrics like supplier innovation pipeline, diversity spend growth, carbon footprint reduction by category, and stakeholder satisfaction scores. These balanced scorecards ensure that category strategies deliver holistic value rather than optimizing for cost alone.
Risk Management and Resilience: From Periodic Assessment to Continuous Vigilance
In 2026’s volatile business landscape, procurement risk management and supply chain resilience have moved from periodic priorities to continuous operational imperatives. Geopolitical tensions, tariff volatility, climate events, cyber threats, and market fluctuations pose significant challenges to organizations worldwide. Risk is a daily reality that demands real-time attention.
Companies are turning to advanced technologies and diversification strategies to enhance their risk assessment capabilities and strengthen their supply chains. The organizations that thrive will be those that build resilience into their operating model rather than treating it as a separate initiative.
Geopolitical Risk Assessment
Geopolitical tensions have exposed the fragility of global supply chains in ways that continue to intensify. Trade controls, export restrictions, tariff escalations, and active conflicts are inflating landed costs, blocking key shipping lanes, and squeezing supplies of critical materials. Research indicates that 67% of companies have faced complications in their procurement processes due to geopolitical factors.
To mitigate these risks, organizations are developing comprehensive risk assessment frameworks that go beyond traditional supplier evaluation. These frameworks categorize risks by type and severity, create supplier and regional risk profiles, incorporate real-time geopolitical intelligence, and enable dynamic scenario planning as conditions evolve.
In 2026, procurement teams must navigate an environment where tariff structures can shift rapidly, trade relationships are increasingly politicized, and supply chain decisions carry strategic implications that extend well beyond cost optimization.
Supply Chain Diversification and Regionalization
Diversification has become essential for building resilient supply networks. Organizations are moving away from concentrated sourcing strategies toward multi-hub networks that distribute risk across regions and suppliers. Research shows that 63% of companies have already implemented diversification strategies, while an additional 10% are actively developing such plans.
The shift toward nearshoring and regionalization continues to accelerate. Companies are balancing the efficiency gains of global sourcing against the resilience benefits of shorter, more controllable supply chains. This isn’t about abandoning global networks—it’s about building optionality and redundancy into sourcing strategies.
Key diversification strategies for 2026 include:
- Geographic distribution of critical suppliers across multiple regions to reduce concentration risk
- Multi-sourcing arrangements for essential materials and components
- Nearshoring initiatives that bring production closer to end markets
- Strategic inventory positioning that buffers against disruption without excessive carrying costs
- Supplier ecosystem development that builds relationships with alternative providers before they’re urgently needed
Predictive Risk Management Tools
Predictive analytics and AI are transforming procurement risk management from reactive response to proactive prevention. Research indicates that 66% of organizations now use these technologies for strategic supply chain decisions. These tools analyze vast amounts of structured and unstructured data to forecast potential disruptions and recommend mitigation strategies before problems materialize.
AI-powered risk platforms offer real-time insights into supplier performance, financial health, ESG compliance, and geopolitical exposure. They can monitor news feeds, regulatory changes, weather patterns, and economic indicators to provide early warning of emerging risks. This continuous intelligence enables procurement teams to act on threats while there’s still time to adjust.
Real-Time Monitoring Capabilities
Effective risk management in 2026 requires real-time visibility across the entire supply chain. Research shows that 46% of companies are actively working to enhance visibility and communication throughout their value chain. By implementing advanced monitoring systems, organizations can quickly identify and respond to potential issues before they cascade into major disruptions.
Continuous risk monitoring has become the norm, with organizations tracking:
- Sanctions and compliance alerts that flag potential regulatory violations
- ESG controversies that could impact supplier relationships or brand reputation
- Cyber incidents affecting suppliers or their critical infrastructure
- Financial stress indicators that signal potential supplier instability
- Climate and weather events that threaten production or logistics
Orchestration platforms like Focal Point support this continuous vigilance by integrating supplier risk data into daily workflows. When a risk alert fires, it can automatically trigger review processes, notify relevant stakeholders, and initiate contingency plans.
Building Organizational Resilience
Beyond technological tools, true supply chain resilience requires organizational capabilities and cultural commitment. This means building cross-functional risk response teams, establishing clear escalation protocols, conducting regular scenario planning exercises, and creating a culture where risk awareness is everyone’s responsibility.
The most resilient organizations treat disruption as inevitable and prepare accordingly. They invest in supplier relationships that provide flexibility during crises, maintain strategic reserves of critical materials, and develop the internal capabilities to pivot quickly when conditions change.
A recent CDP study of over 8,000 businesses estimated that the cost of climate-related disruption will reach $120 billion by 2026, with manufacturing, food and beverage, agriculture, and power generation industries most significantly impacted. Procurement teams can combat this risk by building resilience into every sourcing decision, evaluating suppliers not just on cost and quality but on their ability to perform under stress.
ESG in Procurement: From Disclosure to Commercial Accountability
If 2025 was the year sustainable procurement teams proved they could measure, 2026 is the year they must prove they can deliver. ESG metrics have evolved from reporting exercises to commercial constraints, with procurement embedding climate criteria, engagement programs, and enforceable requirements directly into supplier contracts and sourcing decisions.
Gartner predicts that 70% of technology sourcing, procurement, and vendor management leaders will have environmental-sustainability-aligned performance objectives for their functions by 2026.
The Regulatory Imperative
The regulatory landscape also continues to intensify: there are now an estimated 2,500 pieces of ESG legislation globally, and while supply chains aren’t always the primary focus, most of these regulations have direct implications for procurement practices. Laws are broadening in scope to impact more businesses and are increasingly passed with stronger enforcement mechanisms.
Key regulations reshaping procurement in 2026 include the EU Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive (CSDDD), the European Deforestation Regulation (EUDR), the Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM), and expanding disclosure requirements under the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD). In the United States, regulations like the Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act continue to require supply chain due diligence and documentation.
These regulations are raising the bar on transparency, requiring companies to show clearer product-level data, improve emissions reporting, and build stronger due diligence processes. While demanding, many organizations are finding that preparing for upcoming legislation actually drives resilience, better operations, and smarter decision-making.
From Corporate Footprints to Product-Level Accountability
A significant shift in 2026 is the move from corporate-level sustainability reporting to product and service-level accountability. Corporate carbon footprints have become basic hygiene, while product carbon footprints and service carbon footprints are increasingly required in RFPs to enable like-for-like comparison and optimization.
This granularity changes how procurement teams evaluate suppliers and make sourcing decisions. It’s not sufficient for a supplier to simply have a corporate sustainability policy, they must demonstrate the environmental impact of the specific goods and services being procured. Boards, auditors, and lenders expect credible reduction plans and product-level roadmaps, pushing Scope 3 emissions into total cost of ownership models, internal carbon pricing, and financing structures.
ESG Metrics as Performance Indicators
ESG metrics have become essential performance indicators embedded throughout the procurement function. These metrics track supplier diversity, environmental impact, labor practices, and governance compliance. Research from IDC indicates that approximately 80% of IT companies will only source from suppliers that meet environmental, social, and governance mandates.
Leading organizations are tracking ESG performance through comprehensive frameworks:
- Environmental metrics: Carbon emissions by category and supplier, water usage, waste reduction, circular economy participation, renewable energy adoption
- Social metrics: Labor practices compliance, human rights due diligence, community impact, health and safety performance, living wage commitments
- Governance metrics: Anti-corruption compliance, data privacy practices, board diversity, ethical business conduct, transparency in reporting
Sustainable Sourcing as Strategic Advantage
Sustainable sourcing has transformed from a compliance requirement to a competitive advantage. Companies that lead on sustainability are seeing tangible benefits: improved brand reputation, stronger customer loyalty, better access to capital, and enhanced talent attraction. PwC research shows that consumers are willing to pay an average of 9.7% more for sustainably produced or sourced goods, even amid cost-of-living concerns.
McKinsey reports that products with ESG-related claims accounted for 56% of all growth over the past five years, approximately 18% more than expected based on their initial market share. This consumer preference is flowing through to B2B relationships, where enterprise buyers increasingly require sustainability credentials from their suppliers.
Carbon Footprint Reduction
Carbon reduction has become a primary objective for procurement teams. Organizations are implementing strategies to lower emissions across the supply chain, including selecting low-emission alternatives, promoting circular economy practices, optimizing logistics, and working with suppliers on decarbonization roadmaps.
Leading companies have stopped treating value-chain decarbonization as a separate initiative. Instead, they’re embedding it into product design, specifications, sourcing decisions, and supplier requirements, addressing emissions at the points where they are created rather than after the fact.
AI is playing an increasing role in this effort. Agentic AI can translate fragmented emissions data into prioritized category-level and supplier-level actions that balance emissions reduction, cost optimization, margin protection, and supply chain resilience. This intelligence helps procurement teams focus limited resources on the interventions that will have the greatest impact.
The Data Challenge
Procurement’s ability to deliver on ESG commitments depends on data quality and verification. A Deloitte survey of nearly 350 global procurement leaders found that 40% of CPOs said their procurement organizations don’t define or measure their own set of relevant ESG factors, even though 60% do measure suppliers on sustainability to some extent. Closing this gap requires investment in data infrastructure, supplier engagement, and verification capabilities.
The mantra for 2026 is clear: good data will win. Procurement will increasingly own the question: “Can we prove this supplier aligns with our commitments, and not just on paper?”
Supplier Collaboration and Sustainability: The Engine of Sustainable Transformation
Procurement teams have recognized a fundamental truth: sustainable transformation cannot be achieved in isolation. The vast majority of most organizations’ environmental and social impact lies within their supply chains,in Scope 3 emissions, supplier labor practices, and upstream resource consumption. Achieving meaningful sustainability outcomes requires deep collaboration with suppliers, not just compliance mandates.
A recent report by Accenture and EcoVadis found that delivering on corporate sustainability goals was the top driver of 71% of sustainable procurement programs, a figure that rose by 13 percentage points between 2021 and 2024. This acceleration reflects growing recognition that supplier collaboration is the engine of sustainable transformation.
Enhanced Supplier Assessment
Supplier assessment frameworks are undergoing a revolution in 2026. They now include detailed ESG criteria across environmental, social, and governance dimensions, enabling a more holistic evaluation of supplier performance and alignment with organizational values.
Effective supplier assessment in 2026 goes beyond questionnaires and self-reported data. Leading organizations are implementing:
- Third-party verification through recognized sustainability ratings and certifications
- On-site audits that validate supplier claims and identify improvement opportunities
- Continuous monitoring of supplier ESG performance through real-time data feeds
- Risk-based assessment tiers that focus verification resources on high-impact suppliers
- Performance benchmarking that compares supplier sustainability against industry standards
This comprehensive approach helps identify areas for improvement and fosters a culture of continuous sustainability enhancement across the supply base.
Driving Innovation Together
Collaborative innovation programs have become a cornerstone of strategic supplier relationships. By working closely with suppliers, companies are co-creating sustainable solutions that benefit both parties and drive meaningful environmental and social impact.
This partnership approach is essential for addressing complex sustainability challenges that no single organization can solve alone. Examples include joint development of lower-carbon materials and processes, shared investment in renewable energy infrastructure, collaborative circular economy initiatives that design products for reuse and recycling, and supplier development programs that build sustainability capabilities across the value chain.
Buyer-led coalitions and pooled Power Purchase Agreements are making renewable electricity a default expectation for strategic suppliers, particularly in manufacturing and logistics. These collaborative models allow smaller suppliers to access renewable energy options that would be unavailable to them individually.
Supplier Enablement and Development
A critical shift in 2026 is the recognition that procurement teams must actively enable supplier sustainability capabilities, not just demand compliance. Many suppliers (particularly small and medium enterprises) lack the resources, expertise, or infrastructure to meet increasingly stringent sustainability requirements on their own.
Leading organizations are investing in supplier enablement through training programs on sustainability measurement and reporting, technical assistance for emissions reduction and efficiency improvements, financing mechanisms that help suppliers invest in sustainable technologies, and knowledge sharing platforms that spread best practices across the supply base.
This enablement approach recognizes that procurement’s sustainability success is directly tied to the capabilities of its supplier ecosystem. Investing in supplier development creates long-term competitive advantage while accelerating progress toward sustainability goals.
Transparency Through ESG Reporting
ESG reporting and transparency have become standard requirements in procurement relationships. Organizations are working closely with suppliers to ensure accurate and comprehensive disclosure of sustainability metrics. This transparency not only meets regulatory demands but also builds trust with stakeholders, customers, and investors.
Digital product passports are emerging as a key tool for enabling this transparency. These digital records provide detailed information about a product’s origin, composition, and environmental impact throughout its lifecycle. They help companies prove their sustainability claims and support initiatives like circular design and end-of-life recycling.
Regulators and customers increasingly want to know exactly what’s in a product, where it came from, and how it was made. That means companies need deeper, more reliable data across the entire value chain. Procurement teams are at the center of this transparency requirement, working with suppliers to capture and verify the information that stakeholders demand.
Technology-Enabled Supplier Collaboration
Technology platforms are transforming how procurement teams collaborate with suppliers on sustainability. Orchestration platforms like Focal Point integrate supplier sustainability data into daily workflows, making ESG considerations a natural part of sourcing decisions, performance reviews, and relationship management.
Agentic AI is being integrated across procurement workflows to continuously generate risk maps, footprint estimates, and decarbonization plans. AI supports the optimization of logistics, sourcing, specifications, and packaging to reduce emissions and cost at scale. This intelligence enables procurement teams to have more productive sustainability conversations with suppliers—backed by data and focused on actionable improvements.
Embedding Sustainability in the Operating Model
The most advanced organizations are moving beyond project-based sustainability initiatives to embed decarbonization and ESG accountability into the procurement operating model itself. This means establishing repeatable mechanisms for sustainability assessment, aligned incentives that reward sustainable outcomes, and connected data flows that link contracting, supplier relationship management, and performance measurement.
When sustainability is embedded in the operating model, rather than managed as a separate initiative, it becomes self-sustaining. Every sourcing decision, supplier review, and contract negotiation naturally incorporates ESG considerations because they’re built into the workflows and systems that procurement teams use every day.
The organizations that achieve this integration will be positioned to deliver on ambitious sustainability commitments while maintaining operational efficiency and competitive performance. Those that continue to treat sustainability as a side project will struggle to keep pace with regulatory requirements, customer expectations, and competitive pressures.
The Procurement Workforce: Building Teams for the Agentic Era
The procurement workforce is undergoing its most significant transformation in decades. We’re witnessing a fundamental shift in how teams are structured, what skills are valued, and how work gets done. As agentic AI takes on tactical and transactional activities, the human side of procurement is being redefined around strategic judgment, relationship management, and orchestration capabilities.
A recent study indicates that 75% of workers across functions now use AI tools at work. This trend is profoundly impacting procurement, driving the need for new skills, new roles, and new organizational structures. The question is no longer whether AI will change procurement jobs, it’s how organizations will redesign their teams to thrive alongside intelligent systems.
The Hybrid Human-Agent Workforce
Procurement’s future is a coordinated operating model where both humans and agents play distinct, complementary roles. As agentic capabilities mature, humans will drive strategy, relationships, and judgment-heavy decisions, while agents handle the executional and tactical load that slows teams down today.
This hybrid model creates a new definition of the procurement role. It’s no longer defined by administrative tasks but by the value it creates across the business. Procurement professionals become orchestrators of intelligent systems, relationship architects with strategic suppliers, and business partners who translate procurement capabilities into enterprise outcomes.
Human Expertise vs. Agent Efficiency:
| Human Expertise | Agent Efficiency |
|---|---|
| Category strategy development | Workflow execution and coordination |
| Complex negotiation | Documentation and record-keeping |
| Relationship management (suppliers + stakeholders) | Data processing and enrichment |
| Alignment to enterprise goals | Compliance monitoring and validation |
| Ethical judgment and exception handling | Routine communication and follow-up |
Procurement Teams and New Organizational Structures
Organizations are adapting by creating more agile, cross-functional team structures to handle modern procurement challenges. Traditional hierarchies built around transactional processing are giving way to networked teams organized around value streams, categories, and strategic initiatives.
We’re seeing a rise in project-based work and flexible arrangements that allow procurement talent to be deployed where it’s needed most. This shift requires new approaches to recruitment, training, retention, and performance management—approaches that value adaptability and continuous learning alongside technical expertise.
Talent Management in the Agentic Era
Talent management in procurement has become more complex and more critical. Organizations must simultaneously upskill existing teams on AI and digital capabilities while attracting new talent with skills that didn’t exist five years ago. This dual challenge requires sustained investment in learning and development.
Successful organizations are breaking down silos between procurement and other functions, fostering innovation through cross-functional collaboration, and investing in training programs that develop both digital fluency and strategic capabilities. They’re also rethinking career paths to reflect the new reality, creating advancement opportunities that don’t require abandoning strategic work for management responsibilities.
Critical Skills for 2026 and Beyond
| Skill | Importance in 2026 | Development Focus |
|---|---|---|
| AI and agent management | Critical | Working effectively with autonomous systems, knowing when to intervene |
| Digital procurement platforms | Essential | System integration, workflow design, orchestration configuration |
| Sustainability management | High and growing | ESG metrics, sustainable sourcing, supplier development |
| Risk management | Essential | Predictive analytics, scenario planning, resilience building |
| Data interpretation | Critical | Translating analytics into actionable business insights |
| Stakeholder influence | Enduring | Cross-functional collaboration, executive communication |
| Strategic negotiation | Enduring | Complex deal structuring, relationship-based value creation |
The Change Management Imperative
As procurement teams navigate these changes, change management remains one of the biggest barriers to successful transformation. Teams often worry that AI agents are designed to replace them, when in reality the highest-performing models are those built to support human specialists.
Organizations that communicate transparently about the role of AI, involve teams in designing new workflows, and demonstrate how automation creates opportunities for more meaningful work will navigate this transition more successfully. Those that impose change without engagement risk resistance, talent attrition, and failed implementations.
The procurement leaders who invest in their people, developing new capabilities while honoring existing expertise, will build the teams that define procurement excellence in 2026 and beyond.

Operational Excellence: The Orchestration Advantage
Operational excellence in procurement has been redefined. It’s now about orchestrating intelligent systems, unified data, and human expertise into a cohesive operating model that delivers strategic value at scale.
Process Automation and Efficiency
Procurement teams are witnessing a transformative shift through workflow automation, with leaders experiencing up to 25% increase in efficiency and 60% reduction in manual processes. But the real breakthrough is intelligent orchestration that connects automated workflows into end-to-end value chains.
Focal Point’s workflow automation capabilities provide enterprise-level functionality from a single window, eliminating the need to switch between multiple systems. Through its innovative Frames system, Focal Point consolidates every activity, person, vendor, contract, KPI, and dollar in one accessible location.
The platform’s orchestration layer integrates seamlessly with existing processes, offering a unified space to manage all procurement needs without disruption. Teams can access everything from request management to supplier evaluation through specialized Frames, each pulling live data and workflow into organized spaces for thinking, planning, and doing.
No-Code Configuration Benefits
Focal Point’s no-code configurations allow procurement teams to customize workflows without technical expertise, making it possible to adapt and evolve processes as needs change. This flexibility enables organizations to eliminate manual tasks and boost productivity without requiring extensive IT support or development resources.
In 2026, this configurability is essential. Business requirements change rapidly, and procurement teams need the ability to modify workflows, add new automation, and adjust processes without waiting for IT development cycles. No-code platforms democratize process improvement, putting control in the hands of the people closest to the work.
The Three-Layer Agent Stack
To achieve true operational excellence with agentic AI, procurement organizations need a three-layer architecture that enables intelligent automation while maintaining control and governance:
1. Cognition Layer (“The Thinking”): Where AI interprets data and performs reasoning, classification, data-driven recommendations, and understanding of unstructured requests. This layer powers the intelligence behind agent decisions.
2. Execution Layer (“The Doing”): Where agents act across systems: intake portals, workflow tools, contract repositories, communication platforms, ERPs, and supplier data providers. Deep integration at this layer is the primary failure point for most AI initiatives; without it, agents can think but cannot act.
3. Orchestration Layer (“The Connecting”): The central coordination system that manages workflow dependencies, compliance requirements, SLA tracking, human approvals, audit trails, and global status visibility. This layer ensures agents operate safely, accurately, and in context, enabling true multi-agent collaboration.
Organizations that invest in all three layers (not just AI tools) will achieve the operational excellence that defines procurement leadership in 2026.
Productivity Improvement Metrics
Organizations implementing comprehensive orchestration and automation solutions are reporting significant improvements:
- 25% increase in overall efficiency
- 60% reduction in manual processes
- Up to $550 million in documented cost savings for large enterprises
- Substantial reduction in time spent switching between systems
- 30-60% faster cycle times on strategic sourcing initiatives
- Improved data quality through automated validation and enrichment
- Stronger compliance through continuous monitoring and audit trails
These results demonstrate that operational excellence is achievable, but only when automation is built on a foundation of unified data, intelligent orchestration, and thoughtful human-AI collaboration.
Data-Driven Decision Making: The Foundation of Intelligent Procurement
In 2026, data has become the fuel that powers every aspect of modern procurement. From AI agent performance to sustainability reporting to risk monitoring, the quality of outcomes depends directly on the quality of underlying data. Organizations that master data management will lead; those that don’t will struggle to keep pace.
Unified Data Management
Focal Point centralizes procurement data into a single, unified platform, ensuring complete visibility across operations. This consolidation eliminates data silos and provides procurement teams with immediate access to critical information, enabling faster and more informed decision-making processes.
The importance of unified data cannot be overstated. Agents can only perform as well as the information they can access, and procurement data is notoriously scattered across ERPs, contract repositories, intake tools, spreadsheets, inboxes, and supplier systems. When underlying data is fragmented, even the most advanced AI produces inconsistent or limited value.
McKinsey’s research on procurement value leakage with generative AI repeatedly emphasizes that data plumbing and clean inputs are the make-or-break factors for AI success. Supplier information management isn’t glamorous, but it’s the fuel that powers everything else.
The Push for True Supplier Master Data
2026 is seeing a harder push toward true single supplier records across ERPs, S2P platforms, SRM tools, and risk systems. Leading organizations are implementing:
- Automated validations for entity verification, banking details, sanctions screening, and certificate management at onboarding
- Persistent enrichment from performance data, audits, third-party risk feeds, and sustainability metrics
- Real-time synchronization across systems to ensure all teams work from the same supplier truth
- Ownership and accountability for data quality with clear governance processes
Without this foundation, AI and advanced analytics simply won’t deliver on their promise. The organizations that treat supplier data as strategic infrastructure (investing accordingly) will outperform those that continue to tolerate fragmentation.
Analytics and Reporting Capabilities
Modern procurement platforms enrich, consolidate, and standardize data, ensuring all information remains accurate and up-to-date. Through comprehensive dashboards, teams can filter and analyze data by status, vendor, category, stakeholder, or any other dimension, providing deep insights into procurement operations and performance.
But static reporting is no longer sufficient. In 2026, leading organizations are moving toward continuous intelligence, real-time analytics that surface insights as conditions change rather than waiting for periodic reviews. This shift enables proactive decision-making and faster response to emerging opportunities or risks.
AI-Powered Analytics
Agentic AI is transforming how procurement teams interact with data. Rather than building reports and analyzing dashboards, procurement professionals can now ask complex, cross-table questions and receive immediate, contextual answers. AI can synthesize information from multiple sources, identify patterns that humans might miss, and recommend actions based on comprehensive analysis.
This capability changes the nature of procurement analytics from retrospective reporting to forward-looking intelligence. Teams can model scenarios, predict outcomes, and optimize decisions in ways that weren’t possible with traditional business intelligence tools.
Performance Measurement Frameworks
Comprehensive performance measurement systems enable continuous monitoring of key performance indicators through:
- Live data tracking in specialized workspaces and dashboards
- Real-time visibility into project status, milestones, and progress
- Category-specific performance metrics aligned with strategic objectives
- Vendor performance tracking across quality, delivery, cost, and sustainability dimensions
- Savings and efficiency measurements that capture both hard and soft value
- Risk and compliance scorecards that provide early warning of emerging issues
This integrated approach to data-driven decision making, powered by unified platforms and intelligent analytics, represents the most significant advancement in procurement technology since the spreadsheet. It provides procurement teams with the tools they need to drive strategic value while maintaining operational efficiency.
Summary: Procurement’s Defining Year
As we move through 2026, the procurement landscape is experiencing a profound transformation driven by agentic AI, orchestration platforms, sustainability imperatives, and workforce evolution. The shifts we’re witnessing aren’t incremental improvements, they represent a fundamental reimagining of how procurement creates value for the enterprise.
Organizations that embrace this change by leveraging advanced platforms like Focal Point are positioned to thrive in this new era. With unified workflow automation, AI-driven insights, intelligent orchestration, and seamless integration capabilities, Focal Point is a catalyst for operational excellence and strategic value creation.
The Key Themes of 2026:
Agentic AI has arrived. We’ve moved beyond chatbots and copilots to autonomous digital workers that can understand context, make decisions, execute actions across systems, and collaborate with humans. The question has shifted from “Should we use AI?” to “Which processes are AI-first by design?”
Orchestration is the differentiator. The organizations achieving the greatest results aren’t those with the most AI tools, they’re those with the best orchestration. Unified platforms that connect data, workflows, and intelligent agents into cohesive operating models are delivering breakthrough performance.
Sustainability has become operational. ESG has evolved from disclosure exercises to commercial accountability. Procurement teams own responsibility for supply chain sustainability outcomes, with carbon metrics, supplier development programs, and verifiable impact embedded into daily operations.
Risk management is continuous. In a world of geopolitical volatility, tariff uncertainty, and climate disruption, periodic risk assessment is obsolete. Leading organizations have built continuous monitoring and response capabilities into their operating models.
The workforce is being redefined. Procurement professionals are becoming orchestrators of intelligent systems and architects of strategic supplier relationships. New roles are emerging, new skills are required, and new organizational structures are taking shape.
Data is the foundation. Every capability we’ve discussed (agentic AI, orchestration, sustainability accountability, risk monitoring) depends on unified, high-quality data. Organizations that master supplier information management will lead; those that don’t will struggle.
As procurement teams navigate the complexities of ESG requirements, workforce transformation, geopolitical uncertainty, and digital innovation, having the right technology partner becomes crucial. The future of procurement isn’t just about cost savings; it’s about creating sustainable value, fostering innovation, building resilience, and driving strategic business outcomes.
The teams that embrace this shift and deliberately design their operating model (people, process, and technology) to match will be the winners in 2026. Those who adapt to this evolution today will lead the procurement revolution of tomorrow.
FAQ
How will agentic AI impact procurement in 2026?
Agentic AI represents a step change from previous AI capabilities. Unlike chatbots or copilots that require human initiation for every action, AI agents can autonomously receive goals, reason with context, make decisions, and execute actions across systems. In procurement, this means intelligent intake triage, automated supplier research, dynamic document generation, and continuous compliance monitoring, all operating with minimal human intervention. However, the most successful implementations keep humans in the loop for strategic decisions, complex negotiations, and exception handling. Organizations must also address data privacy, governance, and responsible AI practices to realize the full benefits.
What are the key skills procurement professionals will need in 2026?
Procurement professionals must master a blend of technical and strategic capabilities. AI fluency and agent management are now essential, understanding how to work effectively alongside autonomous systems and knowing when human judgment must override algorithmic recommendations. Data interpretation skills are critical for translating analytics into actionable business strategies. Digital platform proficiency, including orchestration tools and workflow configuration, is increasingly expected. At the same time, enduring skills like strategic negotiation, stakeholder influence, and supplier relationship management remain vital. The professionals who thrive will combine digital fluency with strategic judgment.
How is strategic procurement evolving in 2026?
Strategic procurement has fully evolved from a cost-cutting function to a value creation engine. CPOs are now enterprise leaders who shape organizational resilience, AI adoption, and supplier ecosystems. The focus has shifted to building long-term, value-driven relationships with suppliers that prioritize innovation, reliability, risk mitigation, and shared sustainability goals. Procurement increasingly influences enterprise strategy through business partnering, digital transformation leadership, and sustainability programs. Metrics have expanded beyond cost savings to include innovation contributions, ESG outcomes, risk mitigation, and stakeholder satisfaction.
What role will sustainability play in procurement in 2026?
Sustainability has moved from disclosure exercises to commercial accountability. Procurement teams now own responsibility for supply chain ESG outcomes, with carbon metrics, supplier development programs, and verifiable impact embedded into daily operations. Product-level carbon footprints are increasingly required in RFPs, and Scope 3 emissions are being integrated into total cost of ownership models. The regulatory environment continues to intensify with legislation like the EU’s CSDDD, EUDR, and CBAM raising requirements for due diligence and transparency. Organizations that lead on sustainability are seeing competitive advantages including improved brand reputation, customer loyalty, and access to capital.
How is risk management in procurement changing in 2026?
Risk management has evolved from periodic assessment to continuous vigilance. With geopolitical tensions, tariff volatility, climate events, and cyber threats as constant factors, procurement teams are implementing real-time monitoring capabilities that track sanctions, ESG controversies, financial stress, and supply disruptions. Predictive analytics and AI-driven tools forecast potential issues before they materialize. Supply chain diversification and regionalization strategies are accelerating, with organizations building multi-hub networks that distribute risk across regions and suppliers. The most resilient organizations treat disruption as inevitable and build response capabilities into their operating models.
What technologies will drive digital transformation in procurement?
Digital transformation in 2026 is defined by orchestration platforms, agentic AI, and unified data layers. Cloud-based orchestration systems provide the central coordination that connects workflows, enables agent deployment, and ensures governance. Composable, API-first architectures are replacing monolithic suites, allowing organizations to integrate best-of-breed solutions around a unified core. Predictive analytics enable continuous intelligence rather than periodic reporting. Unified data management, consolidating supplier information across ERPs, S2P platforms, risk tools, and third-party sources, provides the foundation that makes everything else possible.
What metrics will be used to measure procurement success in 2026?
Procurement success in 2026 is measured through balanced scorecards that go far beyond traditional cost savings. Key metrics include efficiency improvements and cycle time reductions, innovation contributions from supplier partnerships, sustainability outcomes including Scope 3 emissions reduction and ESG compliance, risk mitigation and supply chain resilience indicators, stakeholder satisfaction and cross-functional collaboration effectiveness, and strategic value creation across the enterprise. The most sophisticated organizations are connecting these metrics to business outcomes, demonstrating how procurement performance drives enterprise competitiveness.
How will the procurement workforce change in 2026?
The procurement workforce is transforming into a hybrid human-agent model where humans drive strategy, relationships, and judgment-heavy decisions while AI agents handle tactical execution. New roles are emerging including procurement data translators, AI product owners, and orchestration architects. Organizational structures are becoming more agile and cross-functional. Digital literacy and AI fluency have become baseline requirements rather than optional extras. Successful organizations are investing heavily in upskilling existing teams while attracting new talent with capabilities that didn’t exist five years ago. Change management, helping teams understand how AI augments rather than replaces their expertise, remains critical to successful transformation.
What is an orchestration layer and why does it matter?
An orchestration layer is the central coordination system that manages workflow dependencies, compliance requirements, SLA tracking, human approvals, audit trails, and global visibility across procurement operations. It serves as the connective tissue between AI agents, existing systems, and human decision-makers, ensuring that automation operates safely, accurately, and in context. Without orchestration, AI initiatives remain fragmented point solutions that fail to deliver enterprise-scale value. Platforms like Focal Point provide this orchestration capability, enabling organizations to unify their procurement operations and realize the full potential of intelligent automation.