Understanding the critical distinctions between direct and indirect procurement is essential for optimizing your business operations and enhancing profitability.
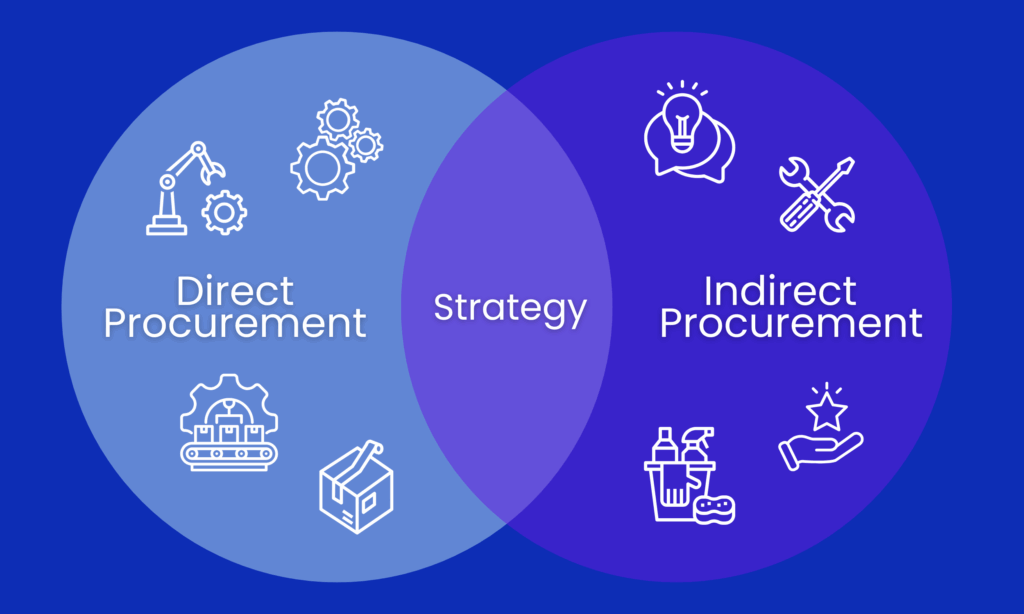
Direct procurement involves purchasing materials, goods, or services that directly become part of your final products or services, such as raw materials and essential components.
In contrast, indirect procurement refers to acquiring goods and services necessary for maintaining your company’s day-to-day operations—like office supplies, consulting services, and software—that do not directly form part of the end product.
These two procurement types require different strategies, management approaches, and often utilize separate systems and workflows.
The distinction matters because each type serves a different purpose in your organization’s value chain.
Direct procurement focuses on the core supplies that are processed and delivered to your customers—items like raw materials, components, and production equipment. Indirect procurement, on the other hand, encompasses everything from office supplies and maintenance services to professional consulting and software subscriptions that keep your business running smoothly behind the scenes.
Key Takeaways
- Direct procurement directly impacts your end product while indirect procurement supports general operations and infrastructure.
- Each procurement type requires different strategies for supplier management, cost control, and operational integration.
- Digital transformation is increasingly essential for optimizing both procurement types through automation and data-driven decision making.
Understanding Direct and Indirect Procurement
Procurement strategies significantly impact an organization’s operational efficiency and financial performance. The distinction between direct and indirect procurement helps businesses allocate resources appropriately and develop specialized approaches for different types of purchases.
What Is Direct Procurement?
Direct procurement refers to purchasing materials, goods, or services that are directly incorporated into a company’s final product or service offering. These purchases directly affect your production capabilities and end product quality.
Raw materials, components, and production equipment fall under this category. For example, in a smartphone manufacturing company, the processors, screens, and batteries would be direct procurement items.
Direct procurement typically:
- Involves high-volume, planned purchases
- Requires close supplier relationships
- Directly impacts revenue generation
- Needs meticulous quality control
- Demands strategic supply chain management
The focus in direct procurement is ensuring consistent supply, maintaining quality standards, and optimizing costs to enhance your final product’s competitiveness in the market.
Defining Indirect Procurement
Indirect procurement encompasses all purchases that support your business operations but don’t directly appear in the final products or services. These purchases keep your business running smoothly behind the scenes.
Examples include office supplies, maintenance services, professional services, travel expenses, utilities, and facilities management. While not part of your end product, these purchases are essential for daily operations.
Characteristics of indirect procurement include:
- Typically smaller, more frequent purchases
- Often decentralized across departments
- Supporting operational continuity
- Wide variety of suppliers and categories
- Less visibility in the overall procurement strategy
Effective indirect procurement helps control overhead costs and ensure your business functions efficiently, though these purchases may seem less critical than direct materials.
Key Differences Between Direct and Indirect Procurement
The fundamental difference between direct and indirect procurement lies in their function and impact on your business outcomes.
Strategic Focus: Direct procurement typically receives more strategic attention as it directly affects product quality and availability. Indirect procurement often focuses more on cost efficiency and process streamlining.
Budget Allocation: Direct procurement usually represents a larger portion of your company’s spending, particularly in manufacturing organizations. Indirect costs, while individually smaller, can accumulate significantly without proper oversight.
Supplier Relationships: Direct procurement often involves fewer suppliers with deeper, long-term relationships. Your indirect procurement may involve numerous vendors with varying relationship depths.
Risk Profile: Supply disruptions in direct procurement immediately impact your production capabilities. Indirect procurement risks are usually less visible but can affect operational efficiency.
Management Approach: Direct procurement typically uses specialized systems focused on supply chain integration. Indirect procurement benefits from spend analysis tools and broader category management approaches.
Procurement Processes and Workflow
Effective procurement processes create a streamlined pathway from identifying needs to receiving goods and services. The structured workflows in both direct and indirect procurement help organizations maintain control over spending while ensuring timely delivery of required resources.
Procurement Process Steps
The procurement process typically begins with identifying needs and requirements. You first determine what resources your organization requires, whether they’re direct materials for manufacturing or indirect supplies for operations.
Next, you develop specifications that clearly outline what you’re looking for from potential suppliers. This critical step ensures you receive quotes and proposals that align with your actual requirements.
Vendor selection follows, where you evaluate potential suppliers based on criteria such as quality, reliability, cost, and delivery capabilities. For direct procurement, this often involves more rigorous assessment since these materials directly impact your final product.
Implementation and contract management round out the process. You execute agreements, issue purchase orders, and establish ongoing supplier relationship management protocols to ensure consistent performance.
Sourcing Strategies
Strategic sourcing forms the backbone of effective procurement management. You can implement several approaches depending on your organizational needs and market conditions.
Single vs. Multiple Sourcing:
- Single sourcing: Deliberate selection of one supplier for specific goods
- Multiple sourcing: Distributing purchases across several vendors to reduce risk
For direct procurement, you might favor long-term partnerships with fewer suppliers to ensure consistency in product quality. Indirect procurement often benefits from competitive bidding across multiple vendors to secure better pricing.
Global sourcing expands your supplier base internationally, potentially offering cost advantages and access to specialized resources. However, you must balance these benefits against increased complexity in logistics and compliance requirements.
Digital sourcing platforms now enable more efficient supplier discovery and relationship management, particularly valuable for organizations managing complex procurement needs.
Purchase Orders and Approvals
Purchase orders (POs) serve as formal documentation of your intent to buy specific goods or services. Your PO should clearly specify quantities, prices, delivery terms, and payment conditions to prevent misunderstandings.
Implementing a structured approval workflow ensures appropriate oversight of procurement activities. You can design approval hierarchies based on:
- Purchase value thresholds
- Department or category-specific authorizations
- Strategic importance of the purchase
Electronic procurement systems streamline this process by routing POs automatically to designated approvers and tracking their progress. This digital approach reduces delays and provides better visibility into pending purchases.
For direct procurement, your approval process might integrate with production planning systems to ensure materials arrive exactly when needed. Indirect procurement typically focuses more on budget compliance and policy adherence in its approval workflows.
Operational Impact of Direct vs. Indirect Procurement
The management of direct and indirect procurement processes significantly influences an organization’s operational structure. Each type affects different aspects of business operations, from supply chain management to resource allocation.
Effect on Supply Chain Management
Direct procurement has immediate implications for your supply chain as it involves materials directly used in production. Delays or quality issues with these materials can halt production lines completely, causing significant operational disruptions.
Your supply chain strategy must account for the critical nature of direct procurement relationships. Building robust supplier relationships and implementing real-time inventory tracking systems can help mitigate risks of production stoppage.
For indirect procurement, supply chain considerations focus more on service reliability and cost-effectiveness. While not production-critical, poor management of indirect supply chains can gradually erode operational efficiency and increase overhead costs.
Key differences in supply chain management:
- Direct: Requires strict quality control protocols and often just-in-time delivery systems
- Indirect: Emphasizes vendor consolidation and service level agreements
- Direct: Often involves global supply networks with higher complexity
- Indirect: Typically allows for more localized supplier relationships
Optimizing Operational Efficiency
Direct procurement optimization directly impacts your production capabilities and product quality. Streamlining direct procurement processes can reduce material costs, which often represent 50-70% of production expenses.
Your procurement strategy should focus on building strong supplier partnerships that can lead to collaborative product development and innovation opportunities.
Indirect procurement optimization, while less visible, significantly affects your organizational agility. By efficiently managing indirect expenses, you can maintain a more cost-effective operational structure.
Consider implementing these efficiency measures:
- Centralized procurement systems that consolidate both direct and indirect purchasing
- Category management strategies tailored to each procurement type
- Digital procurement tools that provide spend visibility across all categories
- Strategic sourcing initiatives that align with broader business objectives
Receive a Free and in-depth demo of Focal Point Procurement from our leadership team, who have over 100 years of procurement experience.
Cost Management and Value Creation
Effective procurement strategies deliver substantial financial benefits through deliberate cost management and value creation initiatives. Both direct and indirect procurement offer unique opportunities to optimize spending and enhance organizational value.
Cost Savings for Direct Procurement
Direct procurement cost management focuses on securing essential materials at optimal prices while maintaining quality standards. You can achieve significant savings through strategic supplier relationships and volume-based negotiations that leverage economies of scale.
Long-term contracts with key suppliers often include tiered pricing structures that reward increased purchase volumes with lower unit costs. These arrangements provide predictability for both parties and help mitigate supply chain disruptions.
Price benchmarking against industry standards helps you identify potential savings opportunities and supports data-driven negotiation tactics. Material substitution and standardization can reduce complexity and drive additional savings without compromising product integrity.
Value engineering initiatives that redesign components or processes can substantially lower direct material costs. When implemented collaboratively with suppliers, these approaches often yield 5-15% cost reductions while maintaining or improving quality specifications.
Cost Reduction in Indirect Spend
Indirect spend management often presents greater cost-saving opportunities due to historically lower scrutiny and fragmented purchasing practices. Consolidating your indirect suppliers can immediately reduce administrative costs and improve buying leverage.
Contract rationalization eliminates redundant services and identifies opportunities for bundled pricing across categories. Category management approaches allow you to develop specialized expertise in key indirect spend areas like IT, facilities, and professional services.
Implementing approval workflows and spend controls helps prevent unauthorized purchases that bypass negotiated agreements. These governance measures typically reduce maverick spending by 15-30%.
Technology solutions like e-procurement platforms and virtual purchasing cards provide visibility and control over indirect spending. Such tools enable policy enforcement at the point of purchase while streamlining processes for end users.
Spend Analysis and Analytics
Comprehensive spend analysis forms the foundation of strategic procurement by revealing patterns and opportunities across your organization’s purchasing activity. Modern analytics tools can categorize and visualize spending across departments, suppliers, and time periods.
Predictive analytics enables you to forecast future needs based on historical patterns, supporting more effective budget planning and inventory management. AI-powered spend analysis can identify anomalies and potential compliance issues before they become problematic.
Supplier performance metrics help quantify value beyond price, including quality, delivery reliability, and innovation contributions. This holistic view ensures cost-saving initiatives don’t inadvertently compromise other value drivers.
Cross-functional spend analysis brings procurement, finance, and operations perspectives together to identify improvement opportunities. These collaborative reviews often reveal interdependencies between direct and indirect spending that create optimization opportunities across your entire supply chain.
Supplier Management and Relationships
The approach to supplier relationships differs significantly between direct and indirect procurement. Direct procurement typically involves fewer, more strategic suppliers with deeper integration, while indirect procurement often manages a broader network of service providers with varying engagement levels.
Supplier Collaboration in Direct Procurement
In direct procurement, supplier collaboration is often intensive and strategic. Your organization likely works closely with suppliers who provide materials directly incorporated into your final products. These relationships tend to be long-term partnerships rather than transactional exchanges.
You’ll find that successful companies often integrate direct suppliers into product development processes. This collaborative approach enables joint innovation, quality improvements, and cost optimization.
Supplier performance metrics are typically more rigorous for direct procurement. You should implement structured evaluation systems focusing on quality, delivery reliability, and technical capabilities.
Many manufacturing firms establish dedicated supplier development programs to enhance critical suppliers’ capabilities. These investments pay dividends through improved component quality and supply chain resilience.
Managing Service Providers
Indirect procurement typically involves managing numerous service providers across diverse categories. Effective management includes clear Service Level Agreements (SLAs) with defined performance metrics, standardized onboarding, and categorization by strategic importance. Digital platforms further enhance visibility and control over your service provider network.
Contract Negotiation and Risk Mitigation
Contract negotiations differ substantially between direct and indirect procurement. For direct materials, your contracts often include detailed specifications, quality requirements, and supply guarantees.
Risk mitigation strategies should address supply disruptions, quality issues, and compliance concerns. For direct suppliers, you might require redundant capacity or safety stock provisions.
With indirect suppliers, contract flexibility and scalability often take precedence. Your agreements should accommodate changing service requirements while maintaining cost control.
Consider implementing systematic supplier risk assessments. These should evaluate financial stability, business continuity capabilities, and compliance with regulations relevant to your industry.
Early supplier involvement in contract discussions can identify potential issues before they become problematic. This collaborative approach to risk management benefits both parties through increased transparency and aligned expectations.
Digital Transformation and Automation in Procurement
The shift toward digital procurement is revolutionizing how organizations manage both direct and indirect procurement processes. Technology adoption enables companies to streamline operations, reduce costs, and make data-driven decisions with unprecedented accuracy.
Procurement Software Solutions
Modern procurement software platforms offer specialized tools to handle both direct and indirect procurement streams. Solutions like Focal Point’s Procurement Platform, supplier relationship management (SRM) tools, and spend analytics platforms help you centralize and optimize purchasing activities.
For direct procurement, specialized solutions focus on BOM management, quality control, and supply chain visibility. These systems integrate with production planning to ensure materials arrive precisely when needed for manufacturing.
Indirect procurement benefits from catalog management systems and self-service portals that streamline the purchasing of office supplies, services, and MRO items. These tools typically include approval workflows that match your organization’s spending policies.
Cloud-based procurement solutions now offer greater flexibility and accessibility, allowing your procurement team to collaborate effectively regardless of location. Many platforms provide mobile capabilities for on-the-go approvals and vendor communications.
Automating Procurement Workflows
Automation eliminates manual processes that traditionally slow procurement activities. By implementing automated workflows, you can reduce processing times by 30-50% while minimizing human error.
Purchase requisitions, approvals, and purchase order generation can be configured to follow predefined rules based on spending thresholds and departmental structures. This ensures compliance while accelerating the procurement cycle.
For direct materials, automation creates seamless connections between demand forecasting, inventory management, and supplier orders. This integration is crucial for maintaining production schedules and avoiding costly disruptions.
Contract management workflows benefit from automation through deadline alerts, renewal reminders, and compliance monitoring. These features help you maximize value from supplier agreements while reducing risk exposure.
AI-powered solutions now enhance automation by identifying spending patterns, suggesting optimal ordering quantities, and flagging potential supply chain issues before they impact operations.
Data Visibility for Better Decision-Making
Digital procurement platforms such as Focal Point provide unprecedented visibility on one dashboard into spending patterns across both direct and indirect categories. Interactive dashboards present key metrics that help you identify cost-saving opportunities and evaluate supplier performance.
Real-time data access allows your procurement team to monitor critical KPIs such as:
- Spend by category/supplier
- Contract compliance rates
- Order cycle times
- Cost variance analysis
- Supplier delivery performance
For direct procurement, enhanced visibility into the supply chain helps you anticipate potential disruptions and implement mitigation strategies before production is affected. Tracking component costs and availability becomes significantly more manageable.
Conclusion
Understanding and strategically managing the differences between direct and indirect procurement can significantly enhance your organization’s performance. Effective procurement strategies reduce costs, improve supplier relationships, and streamline operations, ultimately contributing to better profitability and market competitiveness. To achieve these benefits, adopting a robust procurement management solution like Focal Point Procurement is key. Discover how Focal Point can support your procurement goals—book your demo today and move toward greater operational excellence.